Getting Started
Welcome to the smartMFG API documentation! This API allows you to interact with historical and predicted usage data. Before we dive into the details, here's a quick overview of what you need to get started.
Introduction
The smartMFG API is built using Laravel and utilizes Sanctum tokens for authentication. This ensures secure access to the data and services provided by the API. You can create a token to act on behalf of a user.
All requests should be made to https://api.smart-mfg.net/.
Here's the flow for interacting with the API:

1. Create a Token
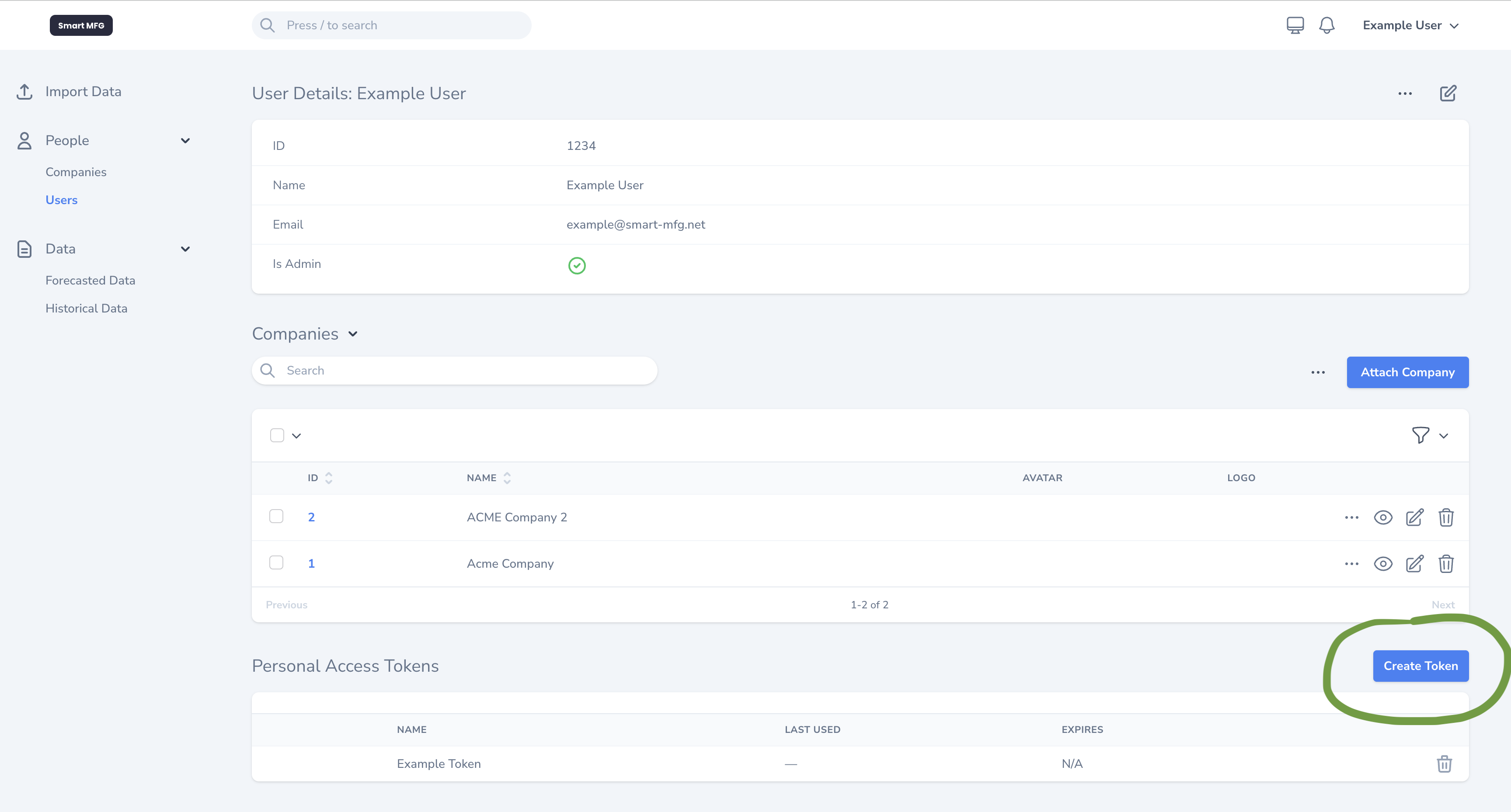
To interact with the API, you'll need to generate a token. Follow these steps to create a token:
- Navigate to the Super Admin Portal.
- Click on a user.
- Scroll to the bottom where you will find a section that lists all the "Personal Access Tokens".
- Click "Create Token" to create a new token for the selected user.
- Make sure to copy the generated token as you'll need it for authentication. You won't be able to see it again.
- Important: Keep your token secure – it allows access to the API on behalf of the user, and doesn't expire until it's deleted.
2. Testing Your Token
Once you have your token, you can test it by making a simple request to the /user endpoint. Here's how you can do it in Python:
import requests
token = "YOUR_GENERATED_TOKEN"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {token}",
"Accept": "application/json"
}
response = requests.get("https://api.smart-mfg.net/user", headers=headers)
print(response.json())
if 200 <= response.status_code < 300:
print("Token is valid!")
else:
print("Failed to authenticate token.")
Replace YOUR_GENERATED_TOKEN with the token you created.
This will return the user details if the token is valid – we'll cover this in more detail in the next section.
3. Understanding POST vs GET Requests
To help you understand the API better, here’s a brief explanation of GET and POST requests:
- GET requests are used to retrieve data from the server. They do not alter the state of the server.
- Get requests have
query parametersthat are appended to the URL.
- Get requests have
- POST requests are used to send data to the server. This can include creating new records or performing actions.
- Post requests have a json
bodythat contains the data to be sent to the server.
- Post requests have a json
4. Understanding Response Codes
When you make a request to the API, you'll receive a response code. Here's what they mean:
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 2xx | Success |
| 200 | OK – the request was successful. |
| 201 | Created – a new resource was created. |
| 204 | No Content – the request was successful, but there is no content to return. |
| 4xx | Client Error |
| 400 | Bad Request – the request was malformed. Something is wrong with the request syntax. |
| 401 | Unauthorized – the request requires user authentication. |
| 403 | Forbidden – the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. |
| 404 | Not Found – the requested resource could not be found. |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity – the request was well-formed but contains semantic errors (Most Common). |
| 429 | Too Many Requests – the user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. |
| 5xx | Server Error |
| 500 | Internal Server Error – the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. |
| 502 | Bad Gateway – the website is down. |
While there are many more response codes, these are the most common ones you'll encounter when working with the smartMFG API.
5. Understanding JSON Responses
When you make a request to the API, you'll receive a 2xx response.
Some requests will return JSON, and some endpoints will simply return a status code – each endpoint's documentation will
specify what to expect.
Here's an example of a successful response:
{
"data": {
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com"
}
}
Any requests that accept input or filters are validated before they are processed.
If there are any errors, the API will return a 422: Unprocessable Entity response with a list of errors:
{
"errors": {
"email": [
"The email field is required."
]
}
}
6. Important Notes
- Each token allows you to act on behalf of a user. A user can have many tokens, but a token can only belong to one user.
- We recommend creating new tokens and delete old ones to ensure security, ideally at least every 6 months.
- If a user has access to multiple companies, always specify a Company ID for historical and forecasted data to ensure you're getting/updating data for the right company. This is included in all examples where it is needed. If not provided, the API will default to the first company the user has access to.
By following these steps, you'll be able to start integrating your machine learning models with the smartMFG API quickly and efficiently.